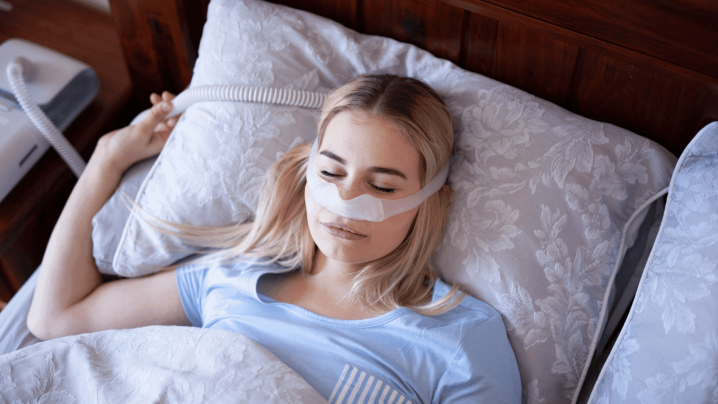
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing throughout the night. These interruptions cause drops in oxygen levels and subsequent sleep disruption, which can lead to excessive fatigue, distraction and even serious health problems during the day. Sleep apnea can affect both men and women and has the potential to affect people of all age groups, although some individuals are at higher risk. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, risk factors and possible treatments for sleep apnea. We will also provide practical advice on the management and prevention of this condition. We will emphasize the importance of awareness and early intervention in the fight against sleep apnea.
Starting with this introduction, we will answer the question "What is Sleep Apnea?" in the next section.
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated cessation of breathing for short periods of time while sleeping. This is caused by partial or complete obstruction of the airways during sleep, repeatedly interrupting the individual's sleep. There are three main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): It is the most common form. Airflow is blocked as a result of relaxation and narrowing of the airways.
- Central Sleep Apnea (SUA): This type occurs because the brain does not send regular breathing commands to the respiratory muscles.
- Mixed Sleep Apnea: It has characteristics of both OUA and SUA.
Sleep apnea severely impairs sleep quality, leading to reduced oxygen levels during the night, which in turn leads to excessive fatigue, distraction and reduced productivity during the daytime. In the long term, left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure and diabetes.
Sleep apnea is usually diagnosed with a sleep study (polysomnography), which records breathing, oxygen levels and other body functions during sleep. This diagnosis is important in determining the type and severity of sleep apnea, as treatment options should be specific to the individual's condition.
Following this definition, in the next section we will discuss the symptoms of sleep apnea in more detail. Being aware of these symptoms is critical for early diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can present with a variety of symptoms. Although these symptoms vary from individual to individual, there are some signs that are common in people with sleep apnea:
- Recurrent Breathlessness Throughout the Night: Breathing stops and restarts during sleep, often accompanied by snoring or choking sounds.
- Gündüz Aşırı Yorgunluk ve Uyuklama: Uykunun defalarca kesilmesi, gündüz saatlerinde aşırı yorgunluğa ve hatta uyanık kalmakta güçlük çekmeye neden olur.
- Snoring: Loud and continuous snoring is common, especially in individuals with obstructive sleep apnea. However, not every snorer may have sleep apnea.
- Morning Headaches: Decreased oxygen levels and poor sleep quality can lead to waking up with a headache in the morning.
- Night Sweats: Abnormally heavy sweating can occur during sleep.
- Concentration Difficulties and Memory Problems: Insufficient sleep can lead to lack of concentration and memory problems during the day.
- Restless sleep: The tendency to wake up frequently, to toss and turn and move during sleep.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Men may have problems such as sexual reluctance or dysfunction.
Symptoms of sleep apnea can often go unnoticed for a long time because most symptoms occur during sleep. Therefore, feedback from your partner or a sleep study may be important. If you have any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to contact a health professional.
Understanding these symptoms is vital for early detection and effective treatment of sleep apnea. In the next section, we take a closer look at the risk factors for sleep apnea and other factors that can lead to this condition.
Risk Factors of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a complex condition that can be influenced by a variety of individual and environmental factors. Some people may be more prone to the condition due to lifestyle choices or genetic tendencies. Understanding the main risk factors that can contribute to the development of sleep apnea is an important step in preventing and managing this health problem:
- Overweight or Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to increased fatty tissue around the throat and narrowing of the airways, which increases the risk of sleep apnea.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of sleep apnea may increase predisposition to this condition.
- Age: With age, muscle tone may decrease and the risk of narrowing of the airways increases. This can increase the likelihood of sleep apnea.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk of developing sleep apnea than women, but the risk also increases in postmenopausal women.
- Alcohol and Smoking: Alcohol can cause narrowing of the airways by increasing muscle relaxation. Smoking can cause inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
- Nasal Congestion Conditions that affect the upper part of the airways, such as allergies, sinusitis or abnormalities in the structure of the nose, can increase the risk of sleep apnea.
- Size of the Neck Circumference: A large neck circumference increases the likelihood of narrowing of the airways. A neck circumference of 17 inches (43 cm) or more in men and 15 inches (38 cm) or more in women can increase the risk.
Measures can be taken to reduce the risk of sleep apnea, such as maintaining a healthy weight, reducing or stopping alcohol and smoking, and managing allergies effectively. If you have risk factors and show symptoms of sleep apnea, it is important to consult a health professional.
In the next section, we will focus on treatment methods for sleep apnea and the various strategies that can be used to manage this condition. These methods can help relieve the symptoms of sleep apnea and improve overall quality of life.
Treatment Methods of Sleep Apnea
Treatment of sleep apnea can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the underlying causes. Treatment should be aimed at relieving symptoms, improving sleep quality and reducing potential health risks. Here are some common treatment methods that can be used to manage sleep apnea:
Lifestyle Changes and Home Precautions
- Lose Weight: Excess weight can increase the risk of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in particular. A healthy diet and regular exercise program can be effective in reducing symptoms.
- Sleeping on your side: Sleeping on your back can cause the tongue and soft palate tissues to block the airway. Sleeping on your side can reduce this risk.
- Reduce Alcohol and Smoking: Alcohol increases muscle relaxation, while smoking can cause inflammation in the airways. Reducing or stopping the use of both can improve sleep apnea symptoms.
- Improving Sleep Hygiene: Regular bedtimes and a comfortable sleep environment can lead to better quality sleep.
Positive Airway Pressure Devices (CPAP)
- CPAP devices provide continuous air pressure to keep the airways open during sleep through a mask. This is a particularly effective treatment option for individuals with obstructive sleep apnea.
Oral Instruments
- For some individuals, especially those with mild or moderate OSA, special appliances placed in the mouth can be helpful. These devices help to keep the airways open by gently pushing the jaw forward.
Surgical Options
- Surgery may be needed to correct structural abnormalities caused by sleep apnea. This may include removal of enlarged tonsils or other procedures to widen the airway.
Oxygen Therapy and Stimulants
- For some severe cases, devices may be used to provide supplementary oxygen or to stimulate the nerves.
Treatment of sleep apnea should be customized according to individual needs. One treatment method may not be suitable for everyone. Therefore, if you are showing symptoms of sleep apnea, it is important to see a sleep specialist to assess your condition and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To prevent or manage sleep apnea, in addition to the lifestyle changes mentioned above, regular health check-ups and monitoring of sleep habits are important. Once symptoms of sleep apnea are recognized, early treatment can prevent long-term health problems and significantly improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that has a significant impact on both individual health and overall quality of life. Recognizing the symptoms, being aware of risk factors, and implementing effective treatment methods are critical to managing sleep apnea. Being proactive in treating sleep apnea is an important step in preventing potential health problems and leading a healthier, more energetic life. If you are experiencing symptoms of sleep apnea, it is best to consult a healthcare professional.