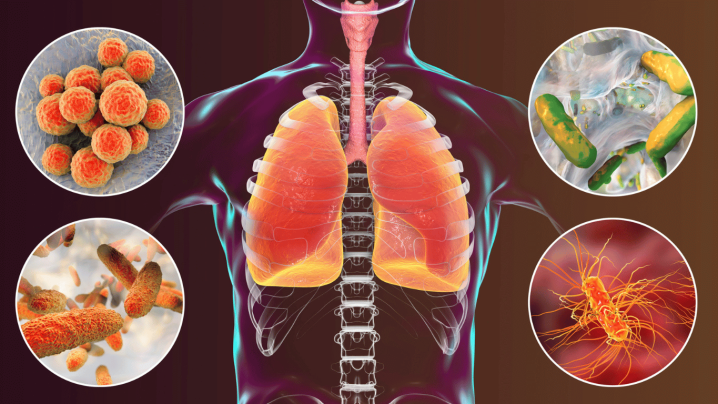
Pneumonia is a disease in which the lungs become infected. The alveoli, the air sacs in the lungs, fill with fluid or pus, making breathing difficult. Bacterial, viral or fungal infections can cause pneumonia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pneumonia can vary from person to person but usually includes
- High fever
- Shivering
- Cough (sometimes with phlegm)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Weakness and fatigue
Risk Factors
The risk of pneumonia is particularly high in the following groups:
- Babies and young children
- Elderly (65 years and older)
- People with chronic diseases (asthma, COPD, heart disease)
- Those with a weak immune system (HIV/AIDS, those undergoing cancer treatment)
Types of Pneumonia
Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is an infection caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae. It usually presents with a sudden onset of high fever, chills and a cough with phlegm.
Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is an infection caused by viruses such as influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Symptoms usually start milder but can become serious.
Mycoplasma Pneumonia
Mycoplasma pneumonia is caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It usually has mild but long-lasting symptoms.
Fungal Pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is an infection caused by fungi. It usually occurs in people with a weak immune system. Symptoms are similar to other types of pneumonia but can be more difficult to treat.
Pneumonia Diagnosis
Physical Examination
The doctor listens to the patient's history and performs a physical examination. Listening to the lungs is important in diagnosing the disease.
Imaging Techniques
- X-ray: It is used to show abnormalities in the lungs.
- Computed Tomography (CT): It provides detailed images and is used in more complex cases.
Laboratory Tests
- Blood Tests It is used to identify signs of infection and which microorganism is causing it.
- Sputum Culture: A sputum sample is taken and analyzed in the laboratory.
Pneumonia Treatment
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It is very important to choose the right antibiotic and use it regularly.
Antiviral and Antifungal Medicines
Antiviral drugs are used for viral pneumonia and antifungal drugs for fungal pneumonia. The duration of treatment and the type of medication depend on the type of infection.
Supportive Treatments
- Oxygen Therapy: Oxygen support is provided for patients with shortness of breath.
- Antipyretics and Painkillers: It is used to control fever and pain.
- Plenty of Fluid Consumption: Drink plenty of water to maintain the body's fluid balance.
Complications of Pneumonia
Pleural Effusion
It occurs when fluid builds up in the space around the lungs and makes breathing difficult.
Bacteremia
It occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream and can lead to serious health problems.
Lung Abscess
It is the formation of a pus-filled cavity in the lungs and can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Respiratory Failure
In severe cases, the lungs cannot provide enough oxygen and a respirator may be needed.
Ways to Prevent Pneumonia
Vaccines
- Pneumococcal Vaccine: Prevents pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria.
- Flu Vaccine: It provides protection against the flu virus and indirectly reduces the risk of viral pneumonia.
Hygiene Precautions
- Hand Washing Hands should be washed frequently with soap and water.
- Mask Use: Wearing a mask, especially in crowded and closed environments, reduces the risk of infection.
Healthy Lifestyle
- Balanced Nutrition: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals should be adopted to strengthen the immune system.
- Non-Smoking Smoking weakens the lungs' defense mechanisms and increases the risk of pneumonia.
Strengthening the Immune System
- Adequate Sleep: Get enough sleep to rest and rejuvenate the body.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity strengthens the immune system.
Pneumonia and COVID-19
Association of COVID-19 with Pneumonia
COVID-19 is a virus that can cause pneumonia. The risk of developing pneumonia is particularly high in severe cases of COVID-19.
Additional Measures Against COVID-19
- Social Distance: Avoiding crowds and maintaining social distance reduces the risk of infection.
- Regular Hand Hygiene: Hands should be washed and disinfected frequently.
- Getting Vaccinated COVID-19 vaccines reduce the risk of a severe course of the disease.
Pneumonia is a serious infectious disease that can be successfully controlled with early diagnosis and treatment. Knowing the risk factors, paying attention to hygiene measures and keeping the immune system strong are important steps in preventing pneumonia. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, more attention should be paid to pneumonia and necessary protective measures should be taken.