The hip joint is one of the largest and most important joints of the human body. This joint, which provides our basic movements such as walking, running and sitting in our daily lives, can be worn or damaged over time for various reasons. Conditions such as aging, traumas and arthritis can cause the hip joint to lose its function, which can seriously affect a person's quality of life. This is where hip replacement, one of the solutions offered by modern medicine, comes into play.
A hip replacement is an artificial joint that replaces a damaged or worn hip joint. This treatment is performed with the aim of reducing pain, increasing joint mobility and thus enabling patients to carry out their daily activities more comfortably and painlessly. Hip replacement surgery is an intervention that can significantly improve quality of life, especially for older people. However, people of all ages may need this treatment.
In this article, we will examine in detail what a hip replacement is, who may need this treatment, the surgical process and the expected recovery afterwards. By shedding light on what is known about hip replacement, we aim to provide guidance to those who are considering this treatment method or who will soon undergo this operation.
What is Hip Replacement?
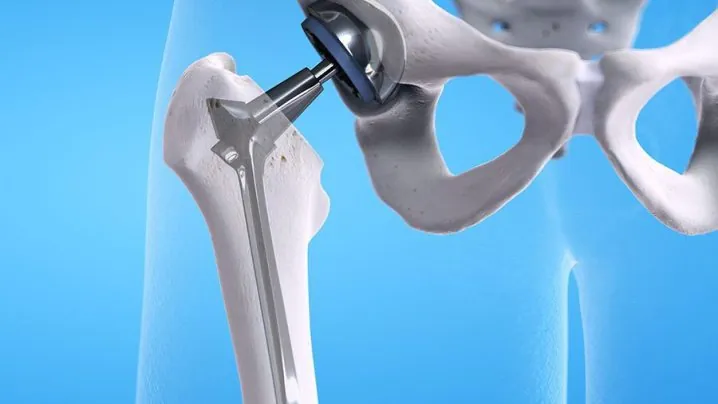
A hip replacement is an artificial joint implant designed to replace a damaged or dysfunctional natural hip joint. These prostheses are usually made of durable materials such as metal, ceramic and plastic and are specially designed to mimic natural joint movements.
Components of a Hip Prosthesis
A hip replacement basically consists of three main components:
- Cup (pelvic component): A round piece, usually made of metal or ceramic, that is placed inside the hip bone.
- Head (Femoral component): A spherical piece, usually made of metal or ceramic, that is inserted into the femur and moves within the cup.
- Astarda: A plastic, ceramic or metal part between the cup and the head that reduces friction and ensures a smooth movement.
Types of Prosthesis
Hip prostheses vary according to the material structure and the way they are placed. The two main types are:
- Total Hip Replacement: This is a treatment in which both the hip bone and the head of the femur are completely replaced.
- Surface Hip Replacement: It is a less invasive approach and is particularly suitable for young and active patients. Only the joint surface is covered here.
Advantages of Hip Replacement
Hip replacement provides the following important advantages:
- Pain Reduction: The prosthesis replaces the damaged joint, significantly reducing pain during movement.
- Increased Mobility: By offering a mobility close to the natural joint, it allows patients to perform their daily activities more comfortably.
- Improved Quality of Life: The ability to move without pain and lead a more active life improves the overall quality of life of patients.
Longevity of Hip Replacement
Modern hip prostheses can maintain their effectiveness for many years thanks to advanced materials and surgical techniques. The lifespan of the prosthesis can vary depending on the patient's age, activity level and the quality of the prosthesis, but can usually last 15-20 years or more.
Hip replacement offers a transformative treatment option for patients, especially in cases of joint disease, accidental injury or excessive wear and tear. Thanks to ever-improving medical technology and surgical techniques, these prostheses provide higher success rates and better outcomes for patients.
Who Needs Hip Replacement Treatment?
Hip replacement is a treatment option for individuals who experience pain and limited mobility, often caused by certain health conditions. People who need this treatment usually experience the following conditions:
Osteoarthritis (Calcification)
- Osteoarthritis is a condition characterized by wear and tear on the joints and is often seen in the elderly.
- Osteoarthritis in the hip joint can cause pain and limitation of movement.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis is a type of inflammatory joint disease in which the immune system attacks the joints.
- This can lead to pain, swelling and loss of function in the hip joint.
Traumatic Arthritis
- Damage to the hip joint caused by accidents or injuries can also lead to traumatic arthritis.
- This damage can lead to inflammation of the joint and subsequent pain and loss of function.
Osteonecrosis
- Osteonecrosis leads to the death of bone tissue due to interrupted blood supply.
- This can cause pain and limitation of movement in the hip joint.
Congenital or Developmental Problems
- Some individuals are born with hip problems that are either congenital or occur during development.
- Such conditions may lead to the need for hip replacement at a later age.
Lifestyle and Other Factors
- Factors such as advanced age, overweight and working in certain professions can also contribute to hip joint wear.
Before undergoing hip replacement treatment, it is important that patients undergo a thorough evaluation by their doctor. This assessment includes factors such as the patient's general state of health, severity of pain, limitation of movement and lifestyle. Treatment is only recommended when all other treatment modalities (medication, physical therapy, exercise, etc.) have failed.
Hip Replacement Surgery Process
Hip replacement surgery is the process of replacing a damaged or dysfunctional hip joint with an artificial joint. This process is customized according to the patient's health condition and needs and consists of several stages:
Preoperative Preparations
- Health Assessment: Prior to surgery, the patient's overall health is thoroughly assessed. This may include heart and lung function tests, blood tests and other necessary medical tests.
- Medications and Diet: Patients are given medications to take and dietary instructions to follow before surgery.
- Physical Preparation: The physical condition of the patient is important for the success of the surgery. If necessary, preoperative physical therapy and exercises may be recommended.
Operation Process
- Anesthesia: Hip replacement surgeries, which are usually performed under general anesthesia, ensure that the patient is completely anesthetized.
- Surgical Procedure: The surgeon removes the damaged hip joint and replaces it with an artificial prosthesis. This process may vary depending on the type of prosthesis and the patient's anatomy.
- Time: Hip replacement surgery usually takes a few hours.
Postoperative Care
- Recovery Room: After surgery, patients are kept under observation for a while.
- Pain Management: Postoperative pain is controlled with medications and other methods.
- Early Mobilization: Patients are encouraged to start moving as early as possible. This reduces the risk of blood clots and speeds up recovery.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy, which begins shortly after surgery, helps the patient adapt to the new hip prosthesis.
- Exercise Programs: Special exercise programs are applied to increase mobility and strength.
- Home Care Instructions: Patients are informed about how to care at home and how to carry out their daily activities.
After hip replacement surgery, most patients can return to their normal life within a few weeks. However, the time to full recovery and to use the full potential of the prosthesis may vary from person to person. To maximize the success of the surgery, it is important that patients strictly follow the doctor's recommendations and rehabilitation programs.