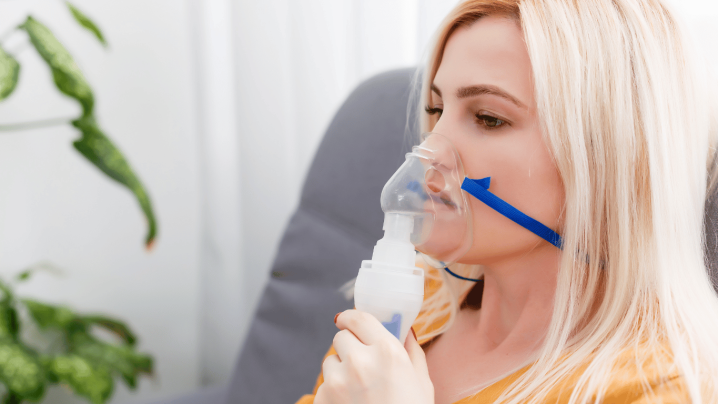
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a serious respiratory condition that affects millions of people. For people with COPD, breathing can become a challenging part of everyday life. However, with the right breathing exercises, COPD patients can improve their breathing, relieve their symptoms and improve their quality of life. In this article, we will review effective breathing exercises for COPD patients and their benefits.
COPD and Breathing Difficulty
COPD is a chronic disease that restricts airflow in the lungs. It is usually caused by smoking or prolonged exposure to air pollution. People with COPD usually experience the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic cough
- Excessive sputum production
- Wheezing
- Feeling of tightness in the chest
These symptoms can make daily activities difficult and reduce quality of life. However, with regular breathing exercises, these symptoms can be alleviated and patients can breathe more easily.
The Importance of Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises offer many benefits for COPD patients:
- Increases lung capacity: Regular exercise helps the lungs to take in and give out more air.
- Reduces shortness of breath: Correct breathing techniques allow patients to breathe more effectively with less effort.
- Improves oxygen utilization: Exercises help the body to use oxygen more efficiently.
- Reduces anxiety: Shortness of breath can cause anxiety, but breathing exercises help to reduce this anxiety.
- Improves overall health: Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health and strengthens the immune system.
Effective Breathing Exercises for COPD Patients
1. Puckered Lip Breathing
This basic technique slows the exhalation and keeps the airways open longer.
How to do it:
- Sit or stand in a comfortable position.
- Take a slow and deep breath in through your nose.
- Pucker your lips like you're whistling.
- Exhale slowly through your pursed lips. The exhalation time should be twice as long as the inhalation time.
- Repeat this exercise several times a day for 5-10 minutes.
2. Diaphragm Breathing
This technique teaches you to use the lower part of the lungs more effectively and reduces the energy spent on breathing.
How to do it:
- Lie on your back or sit in a comfortable chair.
- Put one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach.
- Breathe in slowly through your nose, feel your abdomen swell. Your chest should move minimally.
- Exhale slowly using the puckered lip breathing technique.
- Do this exercise for 5-10 minutes a day.
3. Pursed Lip Breathing Technique
This technique slows the exhalation and keeps the airways open longer.
How to do it:
- Sit in a comfortable position.
- Take a slow and deep breath in through your nose, hold for 2 seconds.
- Pucker your lips, as if you were blowing out a candle.
- Exhale slowly through pursed lips, this should last 4-6 seconds.
- Repeat this exercise several times a day for 5-10 minutes.
4. Coordinated Breathing-Movement Exercises
These exercises help you control your breathing during daily activities.
How to do it:
- Choose an activity (for example, climbing stairs).
- Breathe before starting the activity.
- Exhale while doing the activity (for example, climbing two steps).
- Stop and breathe again.
- Continue in this way, matching your exhalation time to the activity.
5. Chest Expansion Exercises
These exercises increase the flexibility of the rib cage and help you breathe more deeply.
How to do it:
- Sit or stand up straight.
- Let your arms hang by your sides.
- Raise your arms above your head while breathing slowly.
- Hold the breath for a few seconds.
- Lower your arms as you exhale slowly.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
Things to Consider When Exercising
- Slow and controlled: Take your time and breathe slowly and in a controlled manner.
- Stay organized: Try to exercise every day, but do not force yourself.
- Choose a comfortable environment: Do the exercises in a comfortable environment, preferably in the fresh air.
- Find the right position: Make sure you are in a comfortable position, use a chair or pillow if necessary.
- Listen to yourself: If you feel any discomfort, stop exercising and consult your doctor.
- Be patient: It may take time to see the benefits, so practice regularly and be patient.
Integration of Breathing Exercises into COPD Management
Breathing exercises are an important part of the overall management of COPD. However, these exercises alone are not enough. A comprehensive approach to COPD management is needed:
- Medication: Take the medicines prescribed by your doctor regularly.
- Quitting smoking: If you still smoke, get help to quit.
- Healthy eating: Eat a balanced and nutritious diet.
- Regular exercise: In addition to breathing exercises, do physical activities approved by your doctor.
- Stress management: Stress can worsen COPD symptoms. Learn stress-reducing techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Regular check-ups: Go for regular check-ups with your doctor and monitor changes in your condition.
Conclusion
Although COPD is a challenging disease, symptoms can be alleviated and quality of life improved with the right management and exercises. Breathing exercises can help COPD patients improve their breathing, manage their symptoms and make their daily activities more comfortable.
Regularly practicing the breathing exercises described in this article can bring many benefits to COPD patients. However, always consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program. Every COPD patient's condition is different and requires a personalized approach.
Remember, living with COPD can be difficult, but with the right techniques and support it can become easier. Breathing exercises are a powerful tool to help you on this journey. Be patient, practice regularly and you will notice improvement over time.