Allergy in children is a condition that occurs when the immune system overreacts to harmless substances. Allergic reactions can cause a variety of symptoms and negatively affect children's daily lives. The prevalence of allergies has increased in recent years and has become an important health issue for both children and parents. In this article, we will provide detailed information about the symptoms, causes and treatment methods of allergies in children. We aim to raise awareness about allergies and provide parents with practical solutions to protect their children. Dealing with allergies effectively is of great importance for a healthy childhood.
What is Allergy?
Allergy is a condition in which the immune system becomes hypersensitive to certain substances (allergens) and produces various symptoms, including inflammation, in response to these substances. Allergens can be environmental factors such as pollen, dust mites, animal dander, certain foods and some medications. Allergies in children can develop as a result of a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
Common Triggers Causing Allergy in Children:
- Food Allergies: Foods such as milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, shellfish, wheat and soy are the most common food allergens.
- Respiratory Allergies: Airborne allergens such as pollen, house dust mites, mold spores and animal dander.
- Skin Allergies: Direct contact with certain metals such as nickel and substances such as latex can cause skin reactions.
- Insect Stings: The stings of some insects such as bees and wasps can cause allergic reactions.
Allergies in children are characterized by the body reacting to allergens by producing an antibody called IgE. This reaction leads to the release of chemicals such as histamine and causes allergic symptoms.
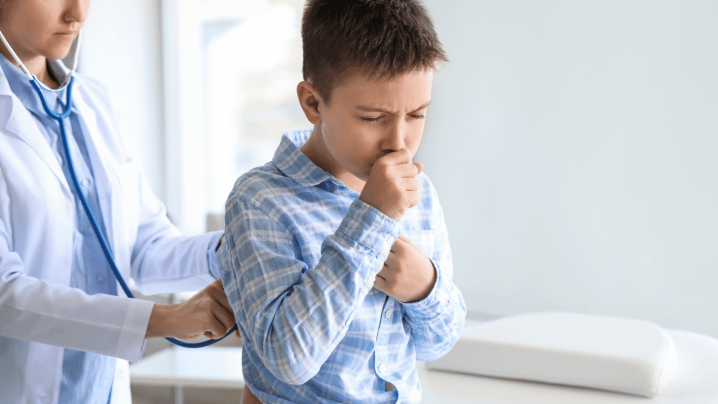
Symptoms of Allergy in Children
Allergic reactions in children can occur in a variety of ways and the symptoms vary depending on the type of allergy. Allergy symptoms can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. Here are the most common types of allergies in children and their symptoms:
Respiratory Allergies
- Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis): Runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion, itchy and watery eyes.
- Asthma: Cough, shortness of breath, wheezing or tightness in the chest.
Food Allergies
- Itching around the mouth: Itching and swelling around the mouth, lips, tongue or throat.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Stomach pain, nausea, vomiting or diarrhea.
- Skin Reactions: Redness, hives (urticaria) or eczema.
- Anafilaksi: Gıda alerjilerinin en ciddi reaksiyonu olan anafilaksi, tüm vücudu etkileyen ve hayati tehlike oluşturan bir durumdur. Anafilaksi belirtileri arasında nefes darlığı, hızlı nabız, döküntü, ve şok bulunur.
Skin Allergies
- Ezema (Atopic Dermatitis): Dry, scaly, itchy skin rashes.
- Contact Dermatitis: Redness, itching and swelling of the skin where it comes into contact with the allergen.
Insect Stings
- Local Reactions: Pain, redness, swelling and itching at the site of the sting.
- Generalized Reactions: In case of hypersensitivity to insect stings, skin rashes, shortness of breath and even anaphylaxis may occur.
When allergy symptoms are recognized, rapid intervention is vital, especially in the case of severe reactions such as anaphylaxis. The severity and type of allergic reactions play a key role in determining the right treatment approach.
Causes of Allergy
Several factors can contribute to the development of allergies in children. Allergic reactions are usually caused by the body being hypersensitive to certain substances (allergens). In this section, we will discuss common causes of allergies and the role of the immune system in this process.
Genetic Factors
There is a genetic predisposition to allergies. If one or both parents are allergic, there is a higher risk that their child will also develop allergies. However, it is not genetically determined which allergens the child will react to.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors to which the child is exposed also play an important role in the development of allergies. Allergens such as pollen, house dust mites, mold spores, animal dander and certain foods can trigger allergic reactions. Cigarette smoke, air pollution and certain chemicals can also increase the risk of allergies.
Role of the Immune System
Allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to substances that are considered harmless. Normally, the immune system protects the body against diseases and infections. However, in allergic individuals, the immune system recognizes certain allergens as dangerous and initiates a defense mechanism against them by producing IgE antibodies. This process leads to the release of chemicals such as histamine and the development of allergic symptoms.
Development of Allergies
When a child is first exposed to an allergen, the immune system recognizes and memorizes these substances. On subsequent exposures, the immune system can react quickly, causing allergic symptoms. Therefore, allergies in children can develop over time and, in some cases, allergies may decrease or increase as the child grows older.
In the next section, we will look at how allergies are diagnosed in children and methods to identify allergens. Allergy diagnosis is the first step in creating an effective treatment plan, allowing the child to lead a healthy life without being exposed to allergic reactions.
Diagnosis of Allergy in Children
Accurate diagnosis of allergies in children is a critical step in creating an effective treatment and management plan. Allergies can present with a variety of symptoms, which can be confused with other health conditions. Therefore, it is important to be evaluated by a qualified health professional. The allergy diagnosis process usually includes a family medical history, physical examination and allergy testing.
Allergy Tests
There are various test methods used to diagnose allergies in children:
- Skin Prick Test: This is one of the most common allergy tests. A small amount of allergen is applied to the surface of the skin and if the skin reacts to this allergen (redness, swelling), the presence of an allergic reaction is detected.
- Blood Tests: Measures the level of antibodies (IgE) produced in the child's blood against allergens. This test can be used as an alternative to or to complement the skin prick test.
- Patch Test: Used to detect contact allergies. The allergen is placed on a patch of skin and the skin reaction is observed for several days.
Diagnosis Process
- Family and Health History: The allergy diagnosis process begins with gathering information about the family history of allergies and the child's reactions to exposure to certain substances.
- Physical Examination: The doctor assesses the child's physical symptoms and looks for possible causes of allergy.
- Allergy Tests: Tests to measure the level of sensitization to specific allergens are an important part of the diagnosis.
Allergen Identification Methods
Allergy tests help to identify which allergens the child reacts to. This information is important for developing allergen avoidance strategies and choosing appropriate treatment when necessary.
Once allergies have been diagnosed, families and doctors can create a plan on how to manage the child's allergies. In the next section, we will look at ways to treat allergies in children and how to manage allergic reactions. This information can help your child live more comfortably with allergies.
Treatment Methods
Treatment of allergies in children depends on the type and severity of the allergy and the individual needs of the child. The aim of treatment is to relieve symptoms, prevent allergic reactions and improve the child's quality of life. Here are some common treatment methods used to manage allergies in children:
Avoiding Allergens
Identifying the allergens that trigger allergic reactions and avoiding them as much as possible is the cornerstone of allergy management. For example, for children with pollen allergy, it is recommended to limit the time spent outdoors on days with high pollen density.
Drug Treatments
- Antihistamines: Help relieve itching, sneezing and runny nose caused by allergic reactions.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, applied as nasal sprays, inhalers or topical creams, control allergic symptoms by reducing inflammation.
- Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: Used in the treatment of respiratory allergies and asthma, these drugs block the action of chemicals that trigger allergic reactions.
Vaccine Therapy (Immunotherapy)
Immunotherapy is allergy shots given regularly over a long period of time to help the body develop tolerance to allergens. This treatment can be particularly effective for children allergic to pollen, house dust mites, animal dander and some insect stings.
Management of Acute Allergic Reactions
- Epinephrine Auto-Injectors: In case of severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, an injection of epinephrine (adrenaline) can be life-saving. It is important that children at risk of allergies and their families are trained on how to use an epinephrine auto-injector and that they always have these injectors with them.
Preventing and Managing Allergies
Prevention and management of allergies in children requires certain measures and changes in daily life. Household allergen control, dietary and nutritional adjustments and lifestyle changes that take into account the child's allergies can reduce the risk of allergic reactions and improve the child's overall health.
Parents of allergic children should know which substances their children are allergic to and be proactive in avoiding allergy triggers. Children's school and caregivers should also be informed about the child's allergies and trained in emergency plans.
Conclusion
Allergies in children can be effectively controlled through symptom management and allergen avoidance strategies. With appropriate treatment and precautions, children diagnosed with allergies can lead healthy and active lives. Dealing with allergies can be challenging for parents and children, but can be managed with the right information and support. If you have questions about your child's allergies or want to learn more about management strategies, consult an allergist. Taking steps for your children's health and well-being will help them have a happier and more comfortable childhood.